Zippers are one of the most common fastening solutions in clothing, bags, outdoor gear, and industrial applications. Among them, metal zippers are particularly popular due to their durability, strength, and aesthetic appeal. At the heart of a zipper’s performance is the zipper slider, which engages and disengages the teeth to open or close the zipper. One critical question for designers, manufacturers, and endusers is: How much tension can a metal zipper slider withstand? Understanding this helps ensure durability, safety, and optimal performance in various applications.
Understanding Metal Zipper Sliders
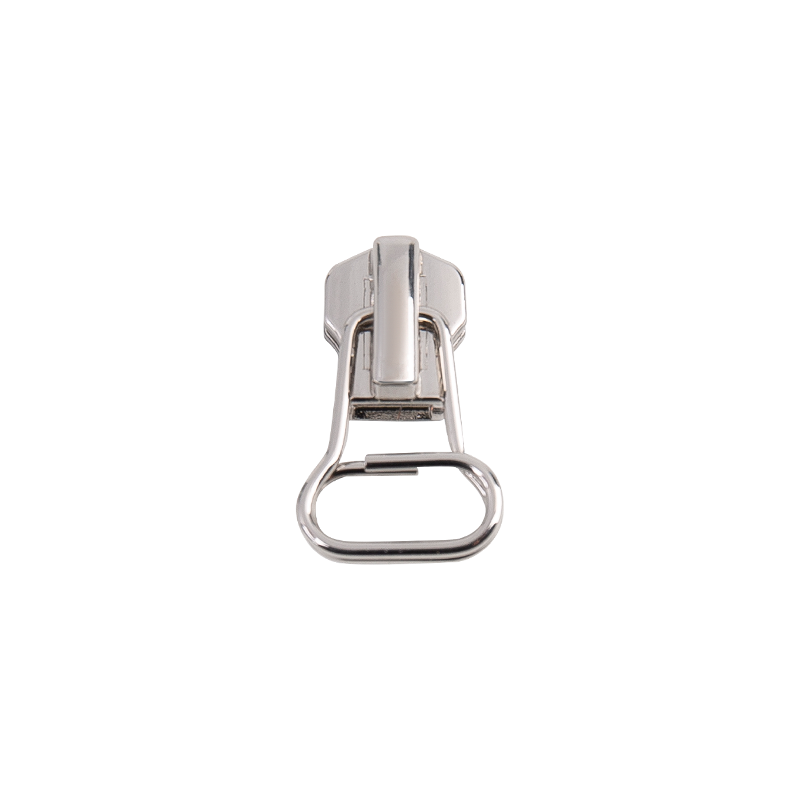
A metal zipper slider is the moving component that runs along the teeth (or coils) of a metal zipper, connecting or separating them. Its performance depends on several factors:
Material: Typically made of brass, zinc alloy, or stainless steel.
Design: Includes pull tabs, body shape, and internal mechanism that aligns the teeth.
Surface Finish: Chrome, nickel, or painted coatings can impact corrosion resistance and longevity.
The slider must withstand both operational stress (during normal opening and closing) and tensile stress (when the zipper is under load), which is especially important for heavyduty applications like backpacks, luggage, jackets, or tents.
Factors Affecting Tension Resistance
The amount of tension a metal zipper slider can withstand is influenced by multiple factors:
1. Slider Material
Brass Sliders: Brass offers good strength and moderate corrosion resistance. They are suitable for mediumduty applications such as jackets or handbags.
Zinc Alloy Sliders: Often plated for durability, zinc alloy sliders are costeffective and suitable for lightweight to medium applications.
Stainless Steel Sliders: Provide the highest strength and corrosion resistance, ideal for heavyduty or outdoor applications.
The choice of material directly impacts the maximum tensile force the slider can tolerate without deformation or failure.
2. Zipper Teeth Size and Type
The slider’s tension resistance also depends on the size and type of the zipper teeth:
HeavyDuty Metal Teeth (e.g., 8, 10): Sliders on these zippers can withstand higher tension because the teeth are stronger and engage more securely.
LightDuty Teeth (e.g., 3, 5): Sliders here are suitable for lighter applications and will fail under excessive load.
A mismatch between slider strength and zipper teeth can reduce overall tension tolerance.
3. Operational Quality
Highquality sliders manufactured with precision tolerances provide better load distribution across the teeth. Poorly made sliders can misalign or deform under tension, reducing the maximum load they can handle.

4. Environmental Factors
Factors such as temperature, humidity, and corrosion can affect the slider’s performance:
Corrosion: Exposure to water, sweat, or chemicals can weaken the metal over time.
Temperature: Extreme heat or cold may make some metals more brittle or deformable.
Abrasion: Frequent use can gradually wear down the internal mechanism, reducing tension resistance.
Typical Tension Ratings
While the exact tension a slider can withstand varies by manufacturer and application, some general guidelines exist:
LightDuty Sliders: Commonly found on clothing, may withstand around 10–30 kg (22–66 lbs) of pulling force.
MediumDuty Sliders: Found on handbags, luggage, or tents, usually tolerate 30–70 kg (66–154 lbs).
HeavyDuty Sliders: Used on backpacks, outdoor gear, or industrial applications, can handle over 100 kg (220 lbs), depending on materials and zipper size.
It’s important to note that these figures include not just the slider, but the combined strength of the teeth, slider, and fabric or material backing. A strong slider alone is not sufficient if the teeth or fabric fail first.
Testing Methods
Manufacturers often perform tensile testing to determine the maximum load a slider can handle. Common methods include:
1. Static Load Test: Applying a gradually increasing pull force until the slider or teeth fail.
2. Repeated Cycle Test: Opening and closing the zipper under load for multiple cycles to assess wear and fatigue.
3. Environmental Simulation: Exposing sliders to moisture, salt spray, or extreme temperatures to evaluate durability under realworld conditions.
These tests help ensure the slider performs reliably under expected loads and conditions.
Applications Requiring HighTension Sliders
Certain applications demand sliders with high tensile resistance:
Outdoor Backpacks: Carrying heavy gear while exposed to rough use.
Luggage and Travel Bags: Withstanding weight and frequent handling.
Protective Clothing: Jackets, overalls, or industrial uniforms under stress.
Tents and Outdoor Gear: High load and environmental exposure.
For these applications, selecting a heavyduty metal slider with strong teeth is essential.
Tips to Maximize Slider Tension Performance
1. Choose the Right Size: Match the slider size with zipper teeth size (8, 10 for heavyduty).
2. Use HighQuality Materials: Stainless steel or brass sliders for high load and durability.
3. Maintain Cleanliness: Dirt, sand, or debris can increase friction and reduce performance.
4. Lubricate When Needed: Small amounts of zipper lubricant can reduce wear under heavy load.
5. Avoid Overloading: Never exceed the design limits of the zipper assembly.
How much tension can a metal zipper slider withstand? The answer varies based on material, teeth size, manufacturing quality, and application conditions. Lightduty sliders may handle 10–30 kg, mediumduty sliders 30–70 kg, and heavyduty sliders can exceed 100 kg. Environmental factors, repeated use, and operational maintenance also play crucial roles in overall performance.
In practical terms, a wellselected metal zipper slider, matched with compatible teeth and fabric, can provide excellent tensile strength and longterm durability, making it suitable for a wide range of consumer, industrial, and outdoor applications. Understanding these factors ensures that the slider will perform reliably and maintain safety and functionality under load.

 en
en  русский
русский 한국어
한국어 get a free quote
get a free quote